Angioplasty and Stent Placement - How Is It Done?
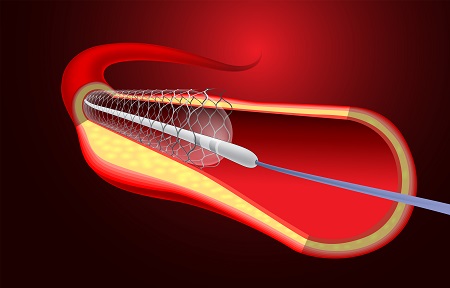 Angioplasty is a medical procedure used to open up arteries that have become blocked due to coronary artery disease. The procedure opens up the blocked artery so that blood flow to the heart is restored without the need for open heart surgery. Angioplasty may be done either as an emergency procedure in the case of a heart attack or as an elective one if a cardiologist finds evidence of heart disease or artery blockage. Once the blockage has been cleared, a tiny expandable metal coil called a stent is usually inserted into the now-open artery to keep it from closing again.
Angioplasty is a medical procedure used to open up arteries that have become blocked due to coronary artery disease. The procedure opens up the blocked artery so that blood flow to the heart is restored without the need for open heart surgery. Angioplasty may be done either as an emergency procedure in the case of a heart attack or as an elective one if a cardiologist finds evidence of heart disease or artery blockage. Once the blockage has been cleared, a tiny expandable metal coil called a stent is usually inserted into the now-open artery to keep it from closing again.
Angioplasty and stent placement are among the most common cardiac procedures and while it is major surgery, it is now an almost routine procedure with cardiology departments of major hospitals performing a number of them every day. For those who have been advised of the procedure, understanding what it involves will ease much of the uncertainty and hesitation that patients often feel.
Also Read: மாரடைப்பின் எச்சரிக்கை அறிகுறிகளை அறியுங்கள் – தாமதிக்காமல் செயல்படுங்கள்!
Preparation
The first stage is to get blood tests and a general health checkup done to see if there are any possible impediments to the surgery that has to be treated first. An angiogram which will enable the surgeon to accurately locate where the blockages are may be done. In some cases, the angioplasty may be done immediately after the angiogram. The surgeon will decide on which is the right procedure.
You will be asked for details of any medication you might be taking and you will be told if you need to stop taking or replace any before the operation. You will also be told about dietary restrictions if any.
The Procedure
The surgery may be done either in an operating theatre or a special room called a catheter lab. The catheter lab will have all the equipment required for the procedure, including x-ray/video equipment to enable the surgeon to monitor the procedure on a screen. Depending on the specifics of the case, the procedure could typically take from 30 minutes to 2 hours.
Once you are in the operating area, this is what will happen:
- You will be asked to lie on your back on the operating table.
- You will be connected to a heart monitor.
- A local anesthetic will be given to numb the operation area.
- An IV line may be inserted into a vein if the surgeon decides that you need to be given a painkiller or a sedative.
- A location on your wrist, arm or groin is identified for making a small incision to access an artery.
- A small tube (sheath) is placed into the artery to keep the incision open during the procedure.
- A slim flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into the opening of the artery and guided toward the opening of the left or right coronary artery.
- The catheter is delicately moved to the area of arterial blockage.
- The catheter has a small balloon at its tip which is gently inflated once the catheter is in position.
- The inflated balloon forces the artery to open and pushes the plaque that caused the blockage away.
- You may feel a few moments of slight discomfort when the balloon is inflated. This is normal and will fade away rapidly. If the pain is uncomfortable, you may be given pain medication.
- If the surgeon decides that a stent is required to keep the artery open and prevent future blockage, a stent will be placed in the now-open part of the artery.
- The stent is put in place through the catheter.
- The stent may or may not have a medicated coating on it to prevent scar tissue from forming inside it.
- When the stent is in place and the surgeon is satisfied that the blood flow through the artery is good, the catheter (and the balloon) will be removed.
- The incision made to insert the catheter will be closed.
Also Read: How Good Sleep Can Keep Your Heart Healthy
After the Procedure
- After the surgery, you will be taken to a recovery area where you will be required to stay in bed and your condition will be closely monitored for signs of any post-surgical problems.
- Your blood pressure will be closely monitored.
- You will be asked to inform the doctor or nurse if you feel any discomfort or pain.
- The time you spend in bed will depend on various factors. The surgeon will decide on this but it is usually between 4 to 6 hours.
- During that time, there may be a recurring urge to urinate. This is normal and caused by medications you may have been given.
- Once the period of bed rest is over and the surgeon is satisfied with your condition, you will be allowed to get out of bed. A nurse will help you to stand and move as you may feel weak at first.
- Your blood pressure will be checked while you are standing.
- You will be asked to drink lots of fluids.
- If there is any residual pain or discomfort, you will be given medication for it.
- Once the doctors are satisfied with your recovery, you will be allowed to go home.
Recovery at Home
Before going home, you will be briefed on the precautions you will need to take and any warning signs of problems you need to look out for. You will be told what you will need to do if any problem should arise and when to contact the doctors.
Follow-up tests and examinations will be required and you will be told when to return to the hospital to undergo them. Once the doctors are satisfied with your recovery, you will be allowed to gradually return to normal activities and work.
Although angioplasty and stent placement are today common procedures, surgery is still a major one. It should be performed only at a hospital with a specialized cardiology department that has cardiologists and surgeons to ensure that you receive world-class care. The hospital must also have the latest technology and medical equipment.
If you have been diagnosed with artery blockage or suspect that you may be suffering from this condition, you must go to a hospital with a cardiology department and surgical facilities. Your condition will be diagnosed and a treatment plan that may involve angioplasty and stent placement will be devised. Knowing that you are in the care of a world-class hospital with the best doctors and facilities will reduce any anxiety you may feel. And reduced stress will make your recovery easier.
All about Angioplasty
- Mar 21, 2023
