Surgery for Thyroid Ailments
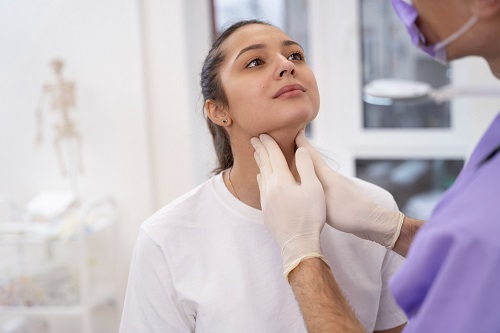 Your thyroid gland is shaped like a butterfly and is in the front of your neck. It is one of the most important glands in the body as it produces hormones that work to control many aspects of your metabolic system ranging from how calories are burnt to how quickly your heart beats (your heart rate). Any problem with this gland can affect your health in a wide variety of ways.
Your thyroid gland is shaped like a butterfly and is in the front of your neck. It is one of the most important glands in the body as it produces hormones that work to control many aspects of your metabolic system ranging from how calories are burnt to how quickly your heart beats (your heart rate). Any problem with this gland can affect your health in a wide variety of ways.
Types of Thyroid Conditions
Thyroid problems can be divided into two main categories:
- Hypothyroidism:In this condition, the gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. Among the many symptoms of this condition are:
- Exhaustion
- Sensitivity to cold
- Dry skin
- Weight gain
- Constipation
- Hair loss
- Muscle pain and stiffness
- And many more
- Hyperthyroidism: This is a condition in which the gland produces an excessive amount of the hormone. Common symptoms are often similar to hypothyroidism but also include:
- Anxiety
- Frequent bowel movements
- Excessive perspiration
- Heart palpitations
- Restlessness
- Insomnia
- And many more
Thyroid gland problems can lead to a large number of health issues, many of them very serious.
Also Read: எண்டோகிரைன் கோளாறுகள் - வகைகள், காரணங்கள், அறிகுறிகள், நோய் கண்டறிதல் மற்றும் சிகிச்சை வகைகள்
Treatment
The treatment for hypothyroidism is hormone replacement therapy to make up for the hormone shortfall. The medication is taken every day at dosages prescribed by a doctor to maintain the correct level of thyroid hormone in the body.
For hyperthyroidism, surgery is the most effective treatment. A procedure called thyroidectomy is performed to remove either part of the gland (partial thyroidectomy) or the complete gland (total thyroidectomy). The type of thyroidectomy will depend on the specifics of your condition and will be decided upon after various examinations and tests are conducted.
If a total gland removal is performed, you will need daily thyroid hormone therapy to give your body the required amount of the hormone. If only a partial gland removal is done, in some cases the remaining part of the gland may produce adequate amounts of the hormone to meet your body’s needs. If it does not, you will need daily hormone therapy. This can only be evaluated after the surgery has been performed.
Preparing for the Surgery
You will normally be prescribed various medications to be taken for a specific period of time prior to surgery. These will work to control the thyroid function and reduce the risk of bleeding and other potential complications. You may be told to avoid eating and drinking anything for a certain amount of time before the surgery. This is a common precaution for surgeries done under general anaesthesia (like this one). Depending on your overall health and other medical issues that may impact surgery, you may be given other instructions on restrictions to follow.
The Procedure
The surgery will begin with you being placed under general anaesthesia. A breathing tube may be inserted into your throat to help you breathe during the surgery. Various monitors will be attached to your body to continually monitor your condition during the procedure. 3 types of surgical procedures may be used. The hospital and your surgeon will decide on which is right for your case:
- Conventional Thyroidectomy: Once the anaesthesia takes effect, the surgeon will make an incision in the lower part of your neck at the centre. If possible, it will be done in a skin crease to hide the scar once the incision heals. Depending on the type of surgery, either all or part of the thyroid gland will be removed. If cancer is suspected, the lymph nodes around the thyroid gland may also be removed. Once the gland is removed, the incision is closed. The procedure typically takes 1 to 2 hours.
- Transoral Thyroidectomy: In this procedure, the thyroid gland is accessed through the mouth.
- Endoscopic Thyroidectomy: This is a form of minimally invasive surgery. Only small incisions are made in the neck. Through one, a tube with a small video camera at the tip will be inserted so that the surgeon can see the gland to be removed. Small surgical instruments will be inserted through the other small incisions and the procedure will be performed. This type of surgery produces less scarring and has a quicker recovery period. However, it may not be suitable for all patients.
Also Read: Whom to See First? General Physician or Specialist?
Recovery
Once the surgery is over, you will be taken to a recovery room where your condition will be observed during the initial recovery period. In some cases, a drain may be placed under the incision for a short time to help the wound drain and for it to be kept dry. From the recovery room, you will be moved to a room or ward where you will typically stay for a day or two. Once the doctors are satisfied with your condition, you will be allowed to return home. You will be prescribed various medications to help with the healing process and to control any post-surgical pain or discomfort. Sore throat and hoarse voice are common for a short time after the procedure.
You will be able to return to normal activities within a few days. Your doctors will tell you when you can start strenuous activities. You will also be told about the daily hormone dosage you will have to take (if this is required).
Thyroid surgery is a common procedure but it is still a major surgery. For that reason, it should be done only at a multispecialty hospital where there are experienced surgeons and the most modern surgical equipment and technology available. A multispecialty hospital also ensures that specialists in other medical disciplines are available to consult about your treatment, if required.
- Dec 13, 2023
