The Role of Hormones in Hair Loss: What You Need to Know
 Hair loss is a common problem affecting both men and women. Most people don’t know that one of the most significant contributors to hair thinning and shedding is hormonal imbalance.
Hair loss is a common problem affecting both men and women. Most people don’t know that one of the most significant contributors to hair thinning and shedding is hormonal imbalance.
Understanding the role of hormones in hair loss can help identify effective treatments.
How Hormones Influence Hair Growth
Hair growth occurs in cycles, consisting of the anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting) phases. Hormonal imbalances can shorten the anagen phase and push more hair follicles into the telogen phase, leading to noticeable thinning. Several key hormones play a role in maintaining healthy hair growth:
- Dihydrotestosterone (DHT): This androgen is derived from testosterone and is the primary cause of androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness). DHT binds to hair follicles, causing them to shrink, weaken, and eventually stop producing hair.
- Estrogen: In women, estrogen helps maintain the anagen phase, promoting thicker and longer hair. A drop in estrogen levels, especially during menopause or postpartum periods, can trigger excessive shedding.
- Thyroid Hormones: An underactive or overactive thyroid gland can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to thinning and brittle strands.
- Cortisol: The stress hormone cortisol can lead to telogen effluvium, a temporary form of hair loss, where large numbers of hair follicles enter the resting phase prematurely.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This condition disrupts hormonal balance in women, increasing androgen levels and leading to hair thinning.
- Pregnancy-Related Hormonal Changes: This can also result in temporary postpartum shedding.
Also Read: Can Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy Help in Hair Restoration?
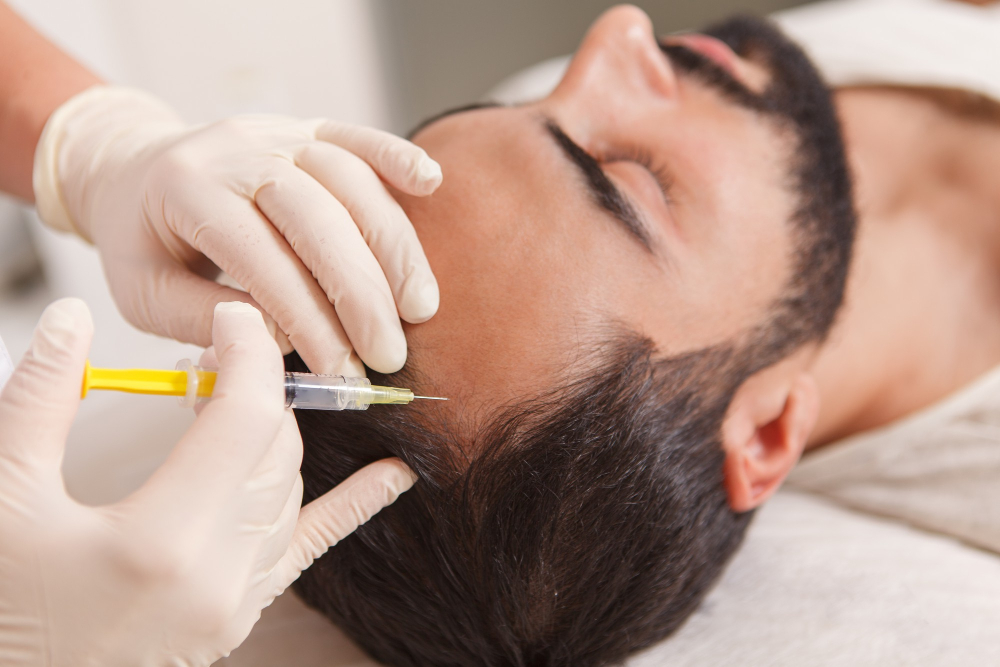
PRP Treatment for Hair Loss
PRP treatment for hair loss has emerged as a promising solution for individuals experiencing hair loss due to hormonal imbalances. PRP treatment involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and injecting the platelet-rich plasma into the scalp.
The growth factors in PRP stimulate dormant hair follicles, promote blood circulation, and enhance hair regrowth. Studies have shown that PRP treatment for hair loss can be particularly beneficial for androgenetic alopecia and thinning caused by hormonal fluctuations.
Since hormones play a crucial role in hair loss, addressing the underlying hormonal imbalance is essential for effective treatment. Lifestyle modifications, stress management, and medical interventions such as hormone therapy or PRP treatment for hair loss can help restore hair growth and prevent further thinning.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do hormones affect hair loss?
Hormones control the hair growth cycle. Imbalances can shorten the growth phase and push hair into a resting phase, causing thinning.
2. What is DHT and how does it cause hair loss?
DHT, derived from testosterone, shrinks hair follicles and is a major factor in pattern baldness.
3. How does estrogen help in hair growth?
Estrogen supports the growth phase of hair, promoting thicker and longer hair. A drop in estrogen can lead to increased shedding.
4. Can thyroid issues lead to hair loss?
Yes, both underactive and overactive thyroid can disrupt the hair cycle, resulting in thinning and brittle hair.
5. What role does stress play in hair loss?
High stress levels raise cortisol, which can trigger a temporary condition called telogen effluvium, leading to increased hair shedding.
6. What is PRP treatment for hair loss?
PRP treatment uses your own blood platelets to stimulate hair follicles, improve circulation, and promote regrowth, especially effective in hormonal hair loss.
- Mar 28, 2025
